Implementing Split Learning (SL), Federated SL and FSL-SAGE in a geo-distributed cross-institute test-bed
NSF AI-EDGE institute: Problem 3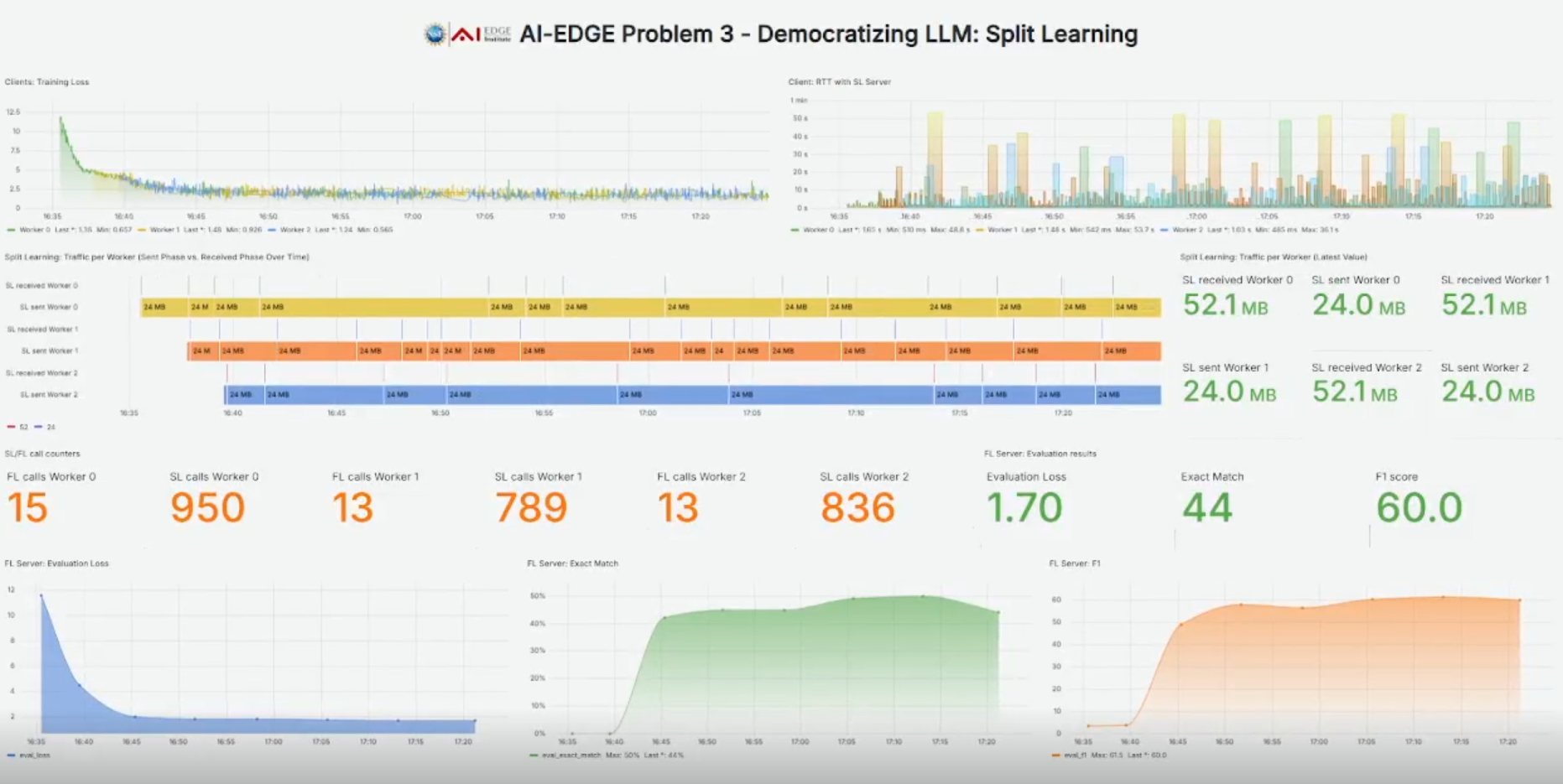
Training today’s large language models (LLMs), often comprising hundreds of billions or even trillions of parameters, demands massive computational and data resources—typically accessible only to hyperscale data centers. However, vast pools of heterogeneous and lower-end GPUs already exist across academic and industrial institutions. Harnessing these distributed resources could democratize large-scale model training, but doing so requires orchestrating computation, communication, and data management across geographically separated sites. The AI-EDGE End-to-End Problem 3 tackles this challenge: how can we collaboratively train and fine-tune LLMs across a federation of edge networks?
Our approach builds on the principles of Federated Learning and Split Learning, combining their strengths into a scalable system that supports distributed pre-training and fine-tuning of LLMs across multiple institutions. While existing FL frameworks focus on full-model training, our federated split learning (FSL) system partitions the model between clients and servers—reducing client memory requirements while enabling collaborative gradient-based updates. We implement this through FSL-SAGE (Federated Split Learning via Smashed Activation Gradient Estimation), a method that estimates server gradients locally to allow asynchronous and communication-efficient training without sacrificing accuracy. The current test-bed spans The Ohio State University, University of Texas at Austin, University of Michigan, and IIT Bombay, each contributing compute and data resources over a geo-distributed network.
This project represents a major step toward decentralized foundation model training—leveraging existing edge hardware for scalable and privacy-preserving AI development. Our framework not only provides an open, extensible platform for collaborative LLM training but also demonstrates that intelligent orchestration and learning design can unlock the latent potential of distributed academic infrastructure. The success of this initiative reflects the combined efforts of the AI-EDGE team, including Prof. Jia (Kevin) Liu, Ziyue Luo, William Wu, Yinglun Xia, and many others.